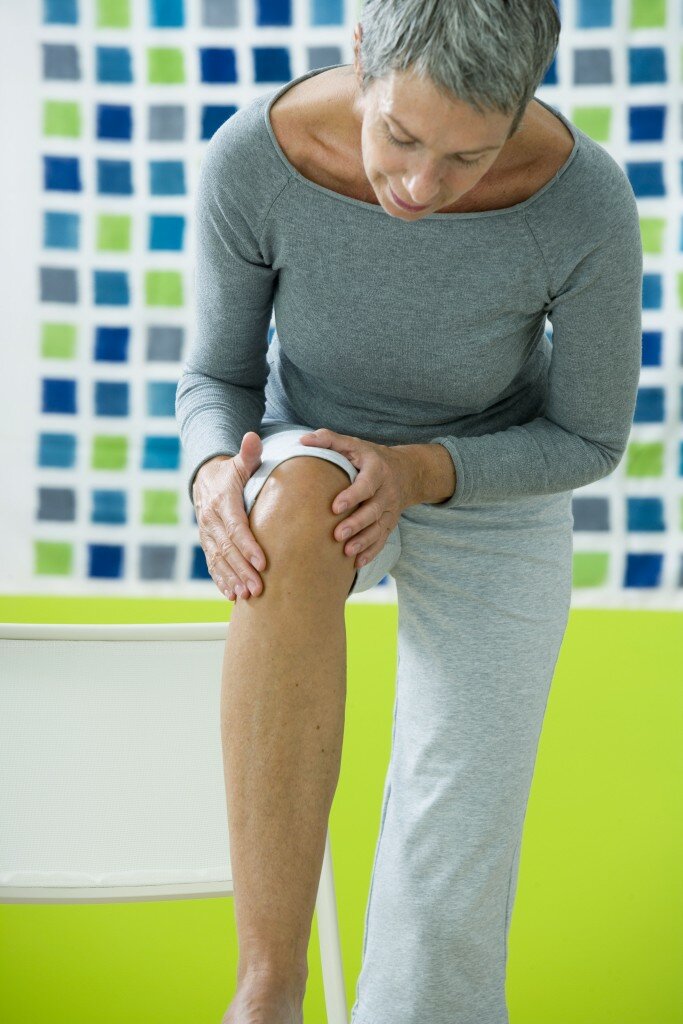
Home Care for Joint Pain
The initial treatment often involves adequate rest, cold compresses and proper medications for controlling inflammation and pain. However, for persistent and severe pain, medical assessment is recommended.
Joint Pain Medications
The medications utilised for treating joint pain will depend on the specific joint pain type: anti-inflammatories or cortisone injections for alleviating inflammation, painkillers for relieving pain, gout medicines for addressing gout, and immunosuppressant drugs for arthritis. Biologic medicines may be recommended for ankylosing spondylitis, psoriatic arthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
Supplements
There is some evidence that supplements such as chondroitin, glucosamine and collagen supplements like Recogen could aid in improving function and relieving joint pain. NutraCeutical Ingredients Pte Ltd mentions these are available in tablet, capsule, liquid or powder formulations.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy can help in strengthening and stabilising the surrounding muscles of your affected joint, as well as improving your range of movement. Common techniques include cold or heat therapy, ultrasound, manipulation and electrical stimulation of the nerves.
Weight Loss
Losing extra weight can aid in alleviating pressure on painful joints. A healthy diet and exercise are crucial, but you must only perform low-impact workouts that will not contribute to more pain. Cycling and swimming are usually recommended since these will make you sweat and work your joints without putting undue pressure on them.
If other conservative treatments do not work, your doctor may recommend surgery, especially if your ligament or cartilage is damaged. However, it is critical to note that regardless of the treatment recommended by your doctor, you should seek medical help immediately if the pain is too intense, if your joint becomes deformed or severely inflamed, or if you cannot move your joint at all.